
GRIMUS helps to remember which forearm bone is fractured and whether the distal ("inferior") or proximal ("superior") part of the other forearm bone is dislocated.

The traditional view is that this injury is most commonly caused by falling onto the back of the hand, but some. In this injury, there is displacement of the bone such that the wrist joint rests in front of its normal anatomic position.

It is useful to note that it is the head of the non-fractured bone that is dislocated. DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES Colles Fracture VS Smith Fracture t.me/MedNoteCollection - medicine medicalstudent doctor mednotecollection orthopedic. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright. Nondisplaced or minimally displaced fractures of the distal wrist, such as Colles and Smith fractures or greenstick, buckle, and physeal fractures in children carpal bone fractures other than. Wrist fracture in which the distal end of the radius is displaced forwards. The Smith’s fracture is a specific type of injury to the forearm bone (the radius) near the wrist joint.
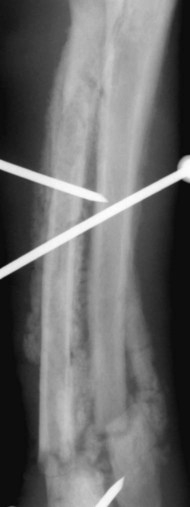
There are several mnemonics for the difference between a Galeazzi and a Monteggia fracture-dislocation:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
